使用 Docker 和 Elasticsearch 构建一个全文搜索应用程序
| 2018-05-01 09:56 收藏: 6
如何在超过 500 万篇文章的 Wikipedia 上找到与你研究相关的文章?
如何在超过 20 亿用户的 Facebook 中找到你的朋友(并且还拼错了名字)?
谷歌如何在整个因特网上搜索你的模糊的、充满拼写错误的查询?
在本教程中,我们将带你探索如何配置我们自己的全文搜索应用程序(与上述问题中的系统相比,它的复杂度要小很多)。我们的示例应用程序将提供一个 UI 和 API 去从 100 部经典文学(比如,《彼得·潘》 、 《弗兰肯斯坦》 和 《金银岛》)中搜索完整的文本。
你可以在这里(https://search.patricktriest.com)预览该教程应用的完整版本。

这个应用程序的源代码是 100% 开源的,可以在 GitHub 仓库上找到它们 —— https://github.com/triestpa/guttenberg-search 。
在应用程序中添加一个快速灵活的全文搜索可能是个挑战。大多数的主流数据库,比如,PostgreSQL 和 MongoDB,由于受其查询和索引结构的限制只能提供一个非常基础的文本搜索功能。为实现高质量的全文搜索,通常的最佳选择是单独的数据存储。Elasticsearch 是一个开源数据存储的领导者,它专门为执行灵活而快速的全文搜索进行了优化。
我们将使用 Docker 去配置我们自己的项目环境和依赖。Docker 是一个容器化引擎,它被 Uber、Spotify、ADP 以及 Paypal 使用。构建容器化应用的一个主要优势是,项目的设置在 Windows、macOS、以及 Linux 上都是相同的 —— 这使我写这个教程快速又简单。如果你还没有使用过 Docker,不用担心,我们接下来将经历完整的项目配置。
我也会使用 Node.js (使用 Koa 框架)和 Vue.js,用它们分别去构建我们自己的搜索 API 和前端 Web 应用程序。
1 - Elasticsearch 是什么?
全文搜索在现代应用程序中是一个有大量需求的特性。搜索也可能是最难的一项特性 —— 许多流行的网站的搜索功能都不合格,要么返回结果太慢,要么找不到精确的结果。通常,这种情况是被底层的数据库所局限:大多数标准的关系型数据库局限于基本的 CONTAINS 或 LIKE SQL 查询上,它仅提供最基本的字符串匹配功能。
我们的搜索应用程序将具备:
- 快速 - 搜索结果将快速返回,为用户提供一个良好的体验。
- 灵活 - 我们希望能够去修改搜索如何执行的方式,这是为了便于在不同的数据库和用户场景下进行优化。
- 容错 - 如果所搜索的内容有拼写错误,我们将仍然会返回相关的结果,而这个结果可能正是用户希望去搜索的结果。
- 全文 - 我们不想限制我们的搜索只能与指定的关键字或者标签相匹配 —— 我们希望它可以搜索在我们的数据存储中的任何东西(包括大的文本字段)。

为了构建一个功能强大的搜索功能,通常最理想的方法是使用一个为全文搜索任务优化过的数据存储。在这里我们使用 Elasticsearch,Elasticsearch 是一个开源的内存中的数据存储,它是用 Java 写的,最初是在 Apache Lucene 库上构建的。
这里有一些来自 Elastic 官方网站 上的 Elasticsearch 真实使用案例。
- Wikipedia 使用 Elasticsearch 去提供带高亮搜索片断的全文搜索功能,并且提供按类型搜索和 “did-you-mean” 建议。
- Guardian 使用 Elasticsearch 把社交网络数据和访客日志相结合,为编辑去提供新文章的公众意见的实时反馈。
- Stack Overflow 将全文搜索和地理查询相结合,并使用 “类似” 的方法去找到相关的查询和回答。
- GitHub 使用 Elasticsearch 对 1300 亿行代码进行查询。
与 “普通的” 数据库相比,Elasticsearch 有什么不一样的地方?
Elasticsearch 之所以能够提供快速灵活的全文搜索,秘密在于它使用反转索引 。
“索引” 是数据库中的一种数据结构,它能够以超快的速度进行数据查询和检索操作。数据库通过存储与表中行相关联的字段来生成索引。在一种可搜索的数据结构(一般是 B 树)中排序索引,在优化过的查询中,数据库能够达到接近线性的时间(比如,“使用 ID=5 查找行”)。
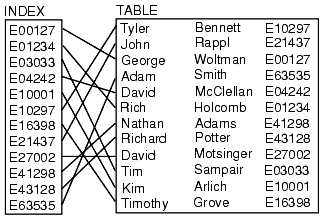
我们可以将数据库索引想像成一个图书馆中老式的卡片式目录 —— 只要你知道书的作者和书名,它就会告诉你书的准确位置。为加速特定字段上的查询速度,数据库表一般有多个索引(比如,在 name 列上的索引可以加速指定名字的查询)。
反转索引本质上是不一样的。每行(或文档)的内容是分开的,并且每个独立的条目(在本案例中是单词)反向指向到包含它的任何文档上。
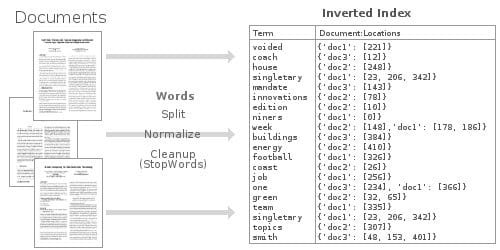
这种反转索引数据结构可以使我们非常快地查询到,所有出现 “football” 的文档。通过使用大量优化过的内存中的反转索引,Elasticsearch 可以让我们在存储的数据上,执行一些非常强大的和自定义的全文搜索。
2 - 项目设置
2.0 - Docker
我们在这个项目上使用 Docker 管理环境和依赖。Docker 是个容器引擎,它允许应用程序运行在一个独立的环境中,不会受到来自主机操作系统和本地开发环境的影响。现在,许多公司将它们的大规模 Web 应用程序主要运行在容器架构上。这样将提升灵活性和容器化应用程序组件的可组构性。

对我来说,使用 Docker 的优势是,它对本教程的作者非常方便,它的本地环境设置量最小,并且跨 Windows、macOS 和 Linux 系统的一致性很好。我们只需要在 Docker 配置文件中定义这些依赖关系,而不是按安装说明分别去安装 Node.js、Elasticsearch 和 Nginx,然后,就可以使用这个配置文件在任何其它地方运行我们的应用程序。而且,因为每个应用程序组件都运行在它自己的独立容器中,它们受本地机器上的其它 “垃圾” 干扰的可能性非常小,因此,在调试问题时,像“它在我这里可以工作!”这类的问题将非常少。
2.1 - 安装 Docker & Docker-Compose
这个项目只依赖 Docker 和 docker-compose,docker-compose 是 Docker 官方支持的一个工具,它用来将定义的多个容器配置 组装 成单一的应用程序栈。
- 安装 Docker - https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/
- 安装 Docker Compose - https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
2.2 - 设置项目主目录
为项目创建一个主目录(名为 guttenberg_search)。我们的项目将工作在主目录的以下两个子目录中。
/public- 保存前端 Vue.js Web 应用程序。/server- 服务器端 Node.js 源代码。
2.3 - 添加 Docker-Compose 配置
接下来,我们将创建一个 docker-compose.yml 文件来定义我们的应用程序栈中的每个容器。
gs-api- 后端应用程序逻辑使用的 Node.js 容器gs-frontend- 前端 Web 应用程序使用的 Ngnix 容器。gs-search- 保存和搜索数据的 Elasticsearch 容器。
version: '3'
services:
api: # Node.js App
container_name: gs-api
build: .
ports:
- "3000:3000" # Expose API port
- "9229:9229" # Expose Node process debug port (disable in production)
environment: # Set ENV vars
- NODE_ENV=local
- ES_HOST=elasticsearch
- PORT=3000
volumes: # Attach local book data directory
- ./books:/usr/src/app/books
frontend: # Nginx Server For Frontend App
container_name: gs-frontend
image: nginx
volumes: # Serve local "public" dir
- ./public:/usr/share/nginx/html
ports:
- "8080:80" # Forward site to localhost:8080
elasticsearch: # Elasticsearch Instance
container_name: gs-search
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:6.1.1
volumes: # Persist ES data in seperate "esdata" volume
- esdata:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
environment:
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
- discovery.type=single-node
ports: # Expose Elasticsearch ports
- "9300:9300"
- "9200:9200"
volumes: # Define seperate volume for Elasticsearch data
esdata:
这个文件定义了我们全部的应用程序栈 —— 不需要在你的本地系统上安装 Elasticsearch、Node 和 Nginx。每个容器都将端口转发到宿主机系统(localhost)上,以便于我们在宿主机上去访问和调试 Node API、Elasticsearch 实例和前端 Web 应用程序。
2.4 - 添加 Dockerfile
对于 Nginx 和 Elasticsearch,我们使用了官方预构建的镜像,而 Node.js 应用程序需要我们自己去构建。
在应用程序的根目录下定义一个简单的 Dockerfile 配置文件。
# Use Node v8.9.0 LTS
FROM node:carbon
# Setup app working directory
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
# Copy package.json and package-lock.json
COPY package*.json ./
# Install app dependencies
RUN npm install
# Copy sourcecode
COPY . .
# Start app
CMD [ "npm", "start" ]
这个 Docker 配置扩展了官方的 Node.js 镜像、拷贝我们的应用程序源代码、以及在容器内安装 NPM 依赖。
我们也增加了一个 .dockerignore 文件,以防止我们不需要的文件拷贝到容器中。
node_modules/
npm-debug.log
books/
public/
请注意:我们之所以不拷贝
node_modules目录到我们的容器中 —— 是因为我们要在容器构建过程里面运行npm install。从宿主机系统拷贝node_modules到容器里面可能会引起错误,因为一些包需要为某些操作系统专门构建。比如说,在 macOS 上安装bcrypt包,然后尝试将这个模块直接拷贝到一个 Ubuntu 容器上将不能工作,因为bcyrpt需要为每个操作系统构建一个特定的二进制文件。
2.5 - 添加基本文件
为了测试我们的配置,我们需要添加一些占位符文件到应用程序目录中。
在 public/index.html 文件中添加如下内容。
<html><body>Hello World From The Frontend Container</body></html>
接下来,在 server/app.js 中添加 Node.js 占位符文件。
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World From the Backend Container'
})
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000
app.listen(port, err => {
if (err) console.error(err)
console.log(`App Listening on Port ${port}`)
})
最后,添加我们的 package.json Node 应用配置。
{
"name": "guttenberg-search",
"version": "0.0.1",
"description": "Source code for Elasticsearch tutorial using 100 classic open source books.",
"scripts": {
"start": "node --inspect=0.0.0.0:9229 server/app.js"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git+https://github.com/triestpa/guttenberg-search.git"
},
"author": "patrick.triest@gmail.com",
"license": "MIT",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/triestpa/guttenberg-search/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/triestpa/guttenberg-search#readme",
"dependencies": {
"elasticsearch": "13.3.1",
"joi": "13.0.1",
"koa": "2.4.1",
"koa-joi-validate": "0.5.1",
"koa-router": "7.2.1"
}
}
这个文件定义了应用程序启动命令和 Node.js 包依赖。
注意:不要运行
npm install—— 当它构建时,依赖会在容器内安装。
2.6 - 测试它的输出
现在一切新绪,我们来测试应用程序的每个组件的输出。从应用程序的主目录运行 docker-compose build,它将构建我们的 Node.js 应用程序容器。
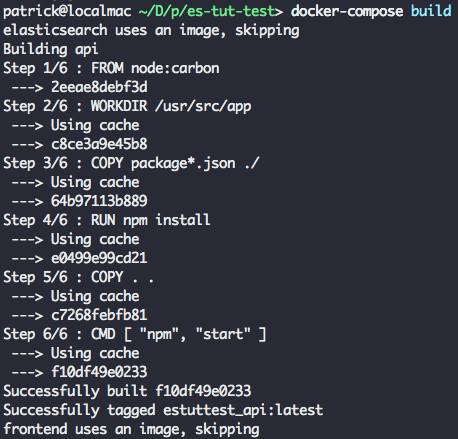
接下来,运行 docker-compose up 去启动整个应用程序栈。
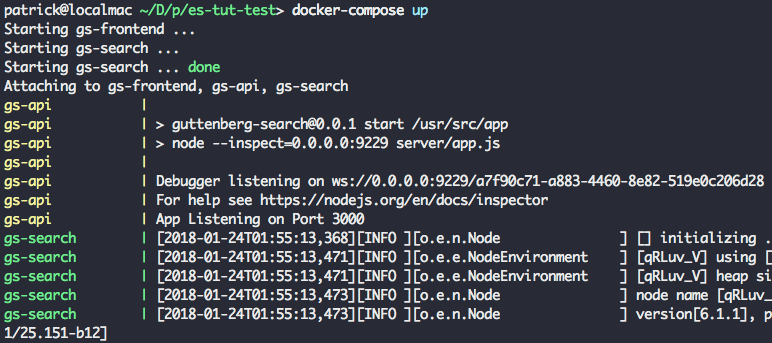
这一步可能需要几分钟时间,因为 Docker 要为每个容器去下载基础镜像。以后再次运行,启动应用程序会非常快,因为所需要的镜像已经下载完成了。
在你的浏览器中尝试访问 localhost:8080 —— 你将看到简单的 “Hello World” Web 页面。
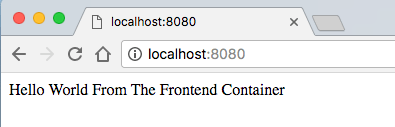
访问 localhost:3000 去验证我们的 Node 服务器,它将返回 “Hello World” 信息。
最后,访问 localhost:9200 去检查 Elasticsearch 运行状态。它将返回类似如下的内容。
{
"name" : "SLTcfpI",
"cluster_name" : "docker-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "iId8e0ZeS_mgh9ALlWQ7-w",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.1.1",
"build_hash" : "bd92e7f",
"build_date" : "2017-12-17T20:23:25.338Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.1.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
如果三个 URL 都显示成功,祝贺你!整个容器栈已经正常运行了,接下来我们进入最有趣的部分。
3 - 连接到 Elasticsearch
我们要做的第一件事情是,让我们的应用程序连接到我们本地的 Elasticsearch 实例上。
3.0 - 添加 ES 连接模块
在新文件 server/connection.js 中添加如下的 Elasticsearch 初始化代码。
const elasticsearch = require('elasticsearch')
// Core ES variables for this project
const index = 'library'
const type = 'novel'
const port = 9200
const host = process.env.ES_HOST || 'localhost'
const client = new elasticsearch.Client({ host: { host, port } })
/** Check the ES connection status */
async function checkConnection () {
let isConnected = false
while (!isConnected) {
console.log('Connecting to ES')
try {
const health = await client.cluster.health({})
console.log(health)
isConnected = true
} catch (err) {
console.log('Connection Failed, Retrying...', err)
}
}
}
checkConnection()
现在,我们重新构建我们的 Node 应用程序,我们将使用 docker-compose build 来做一些改变。接下来,运行 docker-compose up -d 去启动应用程序栈,它将以守护进程的方式在后台运行。
应用程序启动之后,在命令行中运行 docker exec gs-api "node" "server/connection.js",以便于在容器内运行我们的脚本。你将看到类似如下的系统输出信息。
{ cluster_name: 'docker-cluster',
status: 'yellow',
timed_out: false,
number_of_nodes: 1,
number_of_data_nodes: 1,
active_primary_shards: 1,
active_shards: 1,
relocating_shards: 0,
initializing_shards: 0,
unassigned_shards: 1,
delayed_unassigned_shards: 0,
number_of_pending_tasks: 0,
number_of_in_flight_fetch: 0,
task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis: 0,
active_shards_percent_as_number: 50 }
继续之前,我们先删除最下面的 checkConnection() 调用,因为,我们最终的应用程序将调用外部的连接模块。
3.1 - 添加函数去重置索引
在 server/connection.js 中的 checkConnection 下面添加如下的函数,以便于重置 Elasticsearch 索引。
/** Clear the index, recreate it, and add mappings */
async function resetIndex (index) {
if (await client.indices.exists({ index })) {
await client.indices.delete({ index })
}
await client.indices.create({ index })
await putBookMapping()
}
3.2 - 添加图书模式
接下来,我们将为图书的数据模式添加一个 “映射”。在 server/connection.js 中的 resetIndex 函数下面添加如下的函数。
/** Add book section schema mapping to ES */
async function putBookMapping () {
const schema = {
title: { type: 'keyword' },
author: { type: 'keyword' },
location: { type: 'integer' },
text: { type: 'text' }
}
return client.indices.putMapping({ index, type, body: { properties: schema } })
}
这是为 book 索引定义了一个映射。Elasticsearch 中的 index 大概类似于 SQL 的 table 或者 MongoDB 的 collection。我们通过添加映射来为存储的文档指定每个字段和它的数据类型。Elasticsearch 是无模式的,因此,从技术角度来看,我们是不需要添加映射的,但是,这样做,我们可以更好地控制如何处理数据。
比如,我们给 title 和 author 字段分配 keyword 类型,给 text 字段分配 text 类型。之所以这样做的原因是,搜索引擎可以区别处理这些字符串字段 —— 在搜索的时候,搜索引擎将在 text 字段中搜索可能的匹配项,而对于 keyword 类型字段,将对它们进行全文匹配。这看上去差别很小,但是它们对在不同的搜索上的速度和行为的影响非常大。
在文件的底部,导出对外发布的属性和函数,这样我们的应用程序中的其它模块就可以访问它们了。
module.exports = {
client, index, type, checkConnection, resetIndex
}
4 - 加载原始数据
我们将使用来自 古登堡项目 的数据 —— 它致力于为公共提供免费的线上电子书。在这个项目中,我们将使用 100 本经典图书来充实我们的图书馆,包括《福尔摩斯探案集》、《金银岛》、《基督山复仇记》、《环游世界八十天》、《罗密欧与朱丽叶》 和《奥德赛》。

4.1 - 下载图书文件
我将这 100 本书打包成一个文件,你可以从这里下载它 —— https://cdn.patricktriest.com/data/books.zip
将这个文件解压到你的项目的 books/ 目录中。
你可以使用以下的命令来完成(需要在命令行下使用 wget 和 The Unarchiver)。
wget https://cdn.patricktriest.com/data/books.zip
unar books.zip
4.2 - 预览一本书
尝试打开其中的一本书的文件,假设打开的是 219-0.txt。你将注意到它开头是一个公开访问的协议,接下来是一些标识这本书的书名、作者、发行日期、语言和字符编码的行。
Title: Heart of Darkness
Author: Joseph Conrad
Release Date: February 1995 [EBook #219]
Last Updated: September 7, 2016
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
在 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HEART OF DARKNESS *** 这些行后面,是这本书的正式内容。
如果你滚动到本书的底部,你将看到类似 *** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HEART OF DARKNESS *** 信息,接下来是本书更详细的协议版本。
下一步,我们将使用程序从文件头部来解析书的元数据,提取 *** START OF 和 ***END OF 之间的内容。
4.3 - 读取数据目录
我们将写一个脚本来读取每本书的内容,并将这些数据添加到 Elasticsearch。我们将定义一个新的 Javascript 文件 server/load_data.js 来执行这些操作。
首先,我们将从 books/ 目录中获取每个文件的列表。
在 server/load_data.js 中添加下列内容。
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const esConnection = require('./connection')
/** Clear ES index, parse and index all files from the books directory */
async function readAndInsertBooks () {
try {
// Clear previous ES index
await esConnection.resetIndex()
// Read books directory
let files = fs.readdirSync('./books').filter(file => file.slice(-4) === '.txt')
console.log(`Found ${files.length} Files`)
// Read each book file, and index each paragraph in elasticsearch
for (let file of files) {
console.log(`Reading File - ${file}`)
const filePath = path.join('./books', file)
const { title, author, paragraphs } = parseBookFile(filePath)
await insertBookData(title, author, paragraphs)
}
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
}
readAndInsertBooks()
我们将使用一个快捷命令来重构我们的 Node.js 应用程序,并更新运行的容器。
运行 docker-compose up -d --build 去更新应用程序。这是运行 docker-compose build 和 docker-compose up -d 的快捷命令。

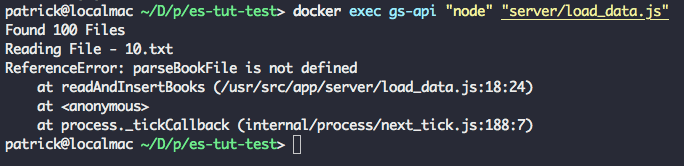
为了在容器中运行我们的 load_data 脚本,我们运行 docker exec gs-api "node" "server/load_data.js" 。你将看到 Elasticsearch 的状态输出 Found 100 Books。
这之后,脚本发生了错误退出,原因是我们调用了一个没有定义的辅助函数(parseBookFile)。
4.4 - 读取数据文件
接下来,我们读取元数据和每本书的内容。
在 server/load_data.js 中定义新函数。
/** Read an individual book text file, and extract the title, author, and paragraphs */
function parseBookFile (filePath) {
// Read text file
const book = fs.readFileSync(filePath, 'utf8')
// Find book title and author
const title = book.match(/^Title:\s(.+)$/m)[1]
const authorMatch = book.match(/^Author:\s(.+)$/m)
const author = (!authorMatch || authorMatch[1].trim() === '') ? 'Unknown Author' : authorMatch[1]
console.log(`Reading Book - ${title} By ${author}`)
// Find Guttenberg metadata header and footer
const startOfBookMatch = book.match(/^\*{3}\s*START OF (THIS|THE) PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK.+\*{3}$/m)
const startOfBookIndex = startOfBookMatch.index + startOfBookMatch[0].length
const endOfBookIndex = book.match(/^\*{3}\s*END OF (THIS|THE) PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK.+\*{3}$/m).index
// Clean book text and split into array of paragraphs
const paragraphs = book
.slice(startOfBookIndex, endOfBookIndex) // Remove Guttenberg header and footer
.split(/\n\s+\n/g) // Split each paragraph into it's own array entry
.map(line => line.replace(/\r\n/g, ' ').trim()) // Remove paragraph line breaks and whitespace
.map(line => line.replace(/_/g, '')) // Guttenberg uses "_" to signify italics. We'll remove it, since it makes the raw text look messy.
.filter((line) => (line && line.length !== '')) // Remove empty lines
console.log(`Parsed ${paragraphs.length} Paragraphs\n`)
return { title, author, paragraphs }
}
这个函数执行几个重要的任务。
- 从文件系统中读取书的文本。
- 使用正则表达式(关于正则表达式,请参阅 这篇文章 )解析书名和作者。
- 通过匹配 “古登堡项目” 的头部和尾部,识别书的正文内容。
- 提取书的内容文本。
- 分割每个段落到它的数组中。
- 清理文本并删除空白行。
它的返回值,我们将构建一个对象,这个对象包含书名、作者、以及书中各段落的数组。
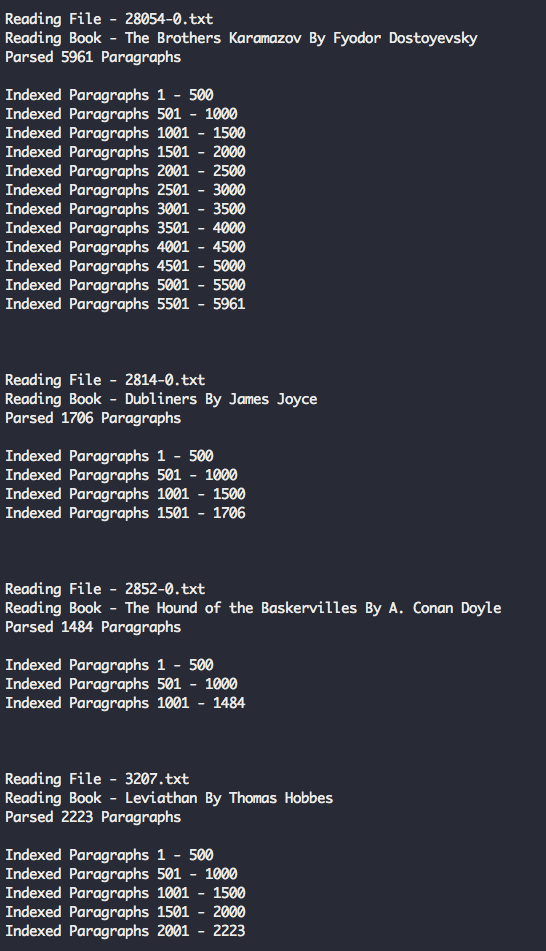
再次运行 docker-compose up -d --build 和 docker exec gs-api "node" "server/load_data.js",你将看到输出同之前一样,在输出的末尾有三个额外的行。

成功!我们的脚本从文本文件中成功解析出了书名和作者。脚本再次以错误结束,因为到现在为止,我们还没有定义辅助函数。
4.5 - 在 ES 中索引数据文件
最后一步,我们将批量上传每个段落的数组到 Elasticsearch 索引中。
在 load_data.js 中添加新的 insertBookData 函数。
/** Bulk index the book data in Elasticsearch */
async function insertBookData (title, author, paragraphs) {
let bulkOps = [] // Array to store bulk operations
// Add an index operation for each section in the book
for (let i = 0; i < paragraphs.length; i++) {
// Describe action
bulkOps.push({ index: { _index: esConnection.index, _type: esConnection.type } })
// Add document
bulkOps.push({
author,
title,
location: i,
text: paragraphs[i]
})
if (i > 0 && i % 500 === 0) { // Do bulk insert in 500 paragraph batches
await esConnection.client.bulk({ body: bulkOps })
bulkOps = []
console.log(`Indexed Paragraphs ${i - 499} - ${i}`)
}
}
// Insert remainder of bulk ops array
await esConnection.client.bulk({ body: bulkOps })
console.log(`Indexed Paragraphs ${paragraphs.length - (bulkOps.length / 2)} - ${paragraphs.length}\n\n\n`)
}
这个函数将使用书名、作者和附加元数据的段落位置来索引书中的每个段落。我们通过批量操作来插入段落,它比逐个段落插入要快的多。
我们分批索引段落,而不是一次性插入全部,是为运行这个应用程序的内存稍有点小(1.7 GB)的服务器
search.patricktriest.com上做的一个重要优化。如果你的机器内存还行(4 GB 以上),你或许不用分批上传。
运行 docker-compose up -d --build 和 docker exec gs-api "node" "server/load_data.js" 一次或多次 —— 现在你将看到前面解析的 100 本书的完整输出,并插入到了 Elasticsearch。这可能需要几分钟时间,甚至更长。
5 - 搜索
现在,Elasticsearch 中已经有了 100 本书了(大约有 230000 个段落),现在我们尝试搜索查询。
5.0 - 简单的 HTTP 查询
首先,我们使用 Elasticsearch 的 HTTP API 对它进行直接查询。
在你的浏览器上访问这个 URL - http://localhost:9200/library/_search?q=text:Java&pretty
在这里,我们将执行一个极简的全文搜索,在我们的图书馆的书中查找 “Java” 这个词。
你将看到类似于下面的一个 JSON 格式的响应。
{
"took" : 11,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 13,
"max_score" : 14.259304,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "library",
"_type" : "novel",
"_id" : "p_GwFWEBaZvLlaAUdQgV",
"_score" : 14.259304,
"_source" : {
"author" : "Charles Darwin",
"title" : "On the Origin of Species",
"location" : 1080,
"text" : "Java, plants of, 375."
}
},
{
"_index" : "library",
"_type" : "novel",
"_id" : "wfKwFWEBaZvLlaAUkjfk",
"_score" : 10.186235,
"_source" : {
"author" : "Edgar Allan Poe",
"title" : "The Works of Edgar Allan Poe",
"location" : 827,
"text" : "After many years spent in foreign travel, I sailed in the year 18-- , from the port of Batavia, in the rich and populous island of Java, on a voyage to the Archipelago of the Sunda islands. I went as passenger--having no other inducement than a kind of nervous restlessness which haunted me as a fiend."
}
},
...
]
}
}
用 Elasticseach 的 HTTP 接口可以测试我们插入的数据是否成功,但是如果直接将这个 API 暴露给 Web 应用程序将有极大的风险。这个 API 将会暴露管理功能(比如直接添加和删除文档),最理想的情况是完全不要对外暴露它。而是写一个简单的 Node.js API 去接收来自客户端的请求,然后(在我们的本地网络中)生成一个正确的查询发送给 Elasticsearch。
5.1 - 查询脚本
我们现在尝试从我们写的 Node.js 脚本中查询 Elasticsearch。
创建一个新文件,server/search.js。
const { client, index, type } = require('./connection')
module.exports = {
/** Query ES index for the provided term */
queryTerm (term, offset = 0) {
const body = {
from: offset,
query: { match: {
text: {
query: term,
operator: 'and',
fuzziness: 'auto'
} } },
highlight: { fields: { text: {} } }
}
return client.search({ index, type, body })
}
}
我们的搜索模块定义一个简单的 search 函数,它将使用输入的词 match 查询。
这是查询的字段分解 -
from- 允许我们分页查询结果。默认每个查询返回 10 个结果,因此,指定from: 10将允许我们取回 10-20 的结果。query- 这里我们指定要查询的词。operator- 我们可以修改搜索行为;在本案例中,我们使用and操作去对查询中包含所有字元(要查询的词)的结果来确定优先顺序。fuzziness- 对拼写错误的容错调整,auto的默认为fuzziness: 2。模糊值越高,结果越需要更多校正。比如,fuzziness: 1将允许以Patricc为关键字的查询中返回与Patrick匹配的结果。highlights- 为结果返回一个额外的字段,这个字段包含 HTML,以显示精确的文本字集和查询中匹配的关键词。
你可以去浏览 Elastic Full-Text Query DSL,学习如何随意调整这些参数,以进一步自定义搜索查询。
6 - API
为了能够从前端应用程序中访问我们的搜索功能,我们来写一个快速的 HTTP API。
6.0 - API 服务器
用以下的内容替换现有的 server/app.js 文件。
const Koa = require('koa')
const Router = require('koa-router')
const joi = require('joi')
const validate = require('koa-joi-validate')
const search = require('./search')
const app = new Koa()
const router = new Router()
// Log each request to the console
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const start = Date.now()
await next()
const ms = Date.now() - start
console.log(`${ctx.method} ${ctx.url} - ${ms}`)
})
// Log percolated errors to the console
app.on('error', err => {
console.error('Server Error', err)
})
// Set permissive CORS header
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
return next()
})
// ADD ENDPOINTS HERE
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000
app
.use(router.routes())
.use(router.allowedMethods())
.listen(port, err => {
if (err) throw err
console.log(`App Listening on Port ${port}`)
})
这些代码将为 Koa.js Node API 服务器导入服务器依赖,设置简单的日志,以及错误处理。
6.1 - 使用查询连接端点
接下来,我们将在服务器上添加一个端点,以便于发布我们的 Elasticsearch 查询功能。
在 server/app.js 文件的 // ADD ENDPOINTS HERE 下面插入下列的代码。
/**
* GET /search
* Search for a term in the library
*/
router.get('/search', async (ctx, next) => {
const { term, offset } = ctx.request.query
ctx.body = await search.queryTerm(term, offset)
}
)
使用 docker-compose up -d --build 重启动应用程序。之后在你的浏览器中尝试调用这个搜索端点。比如,http://localhost:3000/search?term=java 这个请求将搜索整个图书馆中提到 “Java” 的内容。
结果与前面直接调用 Elasticsearch HTTP 界面的结果非常类似。
{
"took": 242,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 93,
"max_score": 13.356944,
"hits": [{
"_index": "library",
"_type": "novel",
"_id": "eHYHJmEBpQg9B4622421",
"_score": 13.356944,
"_source": {
"author": "Charles Darwin",
"title": "On the Origin of Species",
"location": 1080,
"text": "Java, plants of, 375."
},
"highlight": {
"text": ["<em>Java</em>, plants of, 375."]
}
}, {
"_index": "library",
"_type": "novel",
"_id": "2HUHJmEBpQg9B462xdNg",
"_score": 9.030668,
"_source": {
"author": "Unknown Author",
"title": "The King James Bible",
"location": 186,
"text": "10:4 And the sons of Javan; Elishah, and Tarshish, Kittim, and Dodanim."
},
"highlight": {
"text": ["10:4 And the sons of <em>Javan</em>; Elishah, and Tarshish, Kittim, and Dodanim."]
}
}
...
]
}
}
6.2 - 输入校验
这个端点现在还很脆弱 —— 我们没有对请求参数做任何的校验,因此,如果是无效的或者错误的值将使服务器出错。
我们将添加一些使用 Joi 和 Koa-Joi-Validate 库的中间件,以对输入做校验。
/**
* GET /search
* Search for a term in the library
* Query Params -
* term: string under 60 characters
* offset: positive integer
*/
router.get('/search',
validate({
query: {
term: joi.string().max(60).required(),
offset: joi.number().integer().min(0).default(0)
}
}),
async (ctx, next) => {
const { term, offset } = ctx.request.query
ctx.body = await search.queryTerm(term, offset)
}
)
现在,重启服务器,如果你使用一个没有搜索关键字的请求(http://localhost:3000/search),你将返回一个带相关消息的 HTTP 400 错误,比如像 Invalid URL Query - child "term" fails because ["term" is required]。
如果想从 Node 应用程序中查看实时日志,你可以运行 docker-compose logs -f api。
7 - 前端应用程序
现在我们的 /search 端点已经就绪,我们来连接到一个简单的 Web 应用程序来测试这个 API。
7.0 - Vue.js 应用程序
我们将使用 Vue.js 去协调我们的前端。
添加一个新文件 /public/app.js,去控制我们的 Vue.js 应用程序代码。
const vm = new Vue ({
el: '#vue-instance',
data () {
return {
baseUrl: 'http://localhost:3000', // API url
searchTerm: 'Hello World', // Default search term
searchDebounce: null, // Timeout for search bar debounce
searchResults: [], // Displayed search results
numHits: null, // Total search results found
searchOffset: 0, // Search result pagination offset
selectedParagraph: null, // Selected paragraph object
bookOffset: 0, // Offset for book paragraphs being displayed
paragraphs: [] // Paragraphs being displayed in book preview window
}
},
async created () {
this.searchResults = await this.search() // Search for default term
},
methods: {
/** Debounce search input by 100 ms */
onSearchInput () {
clearTimeout(this.searchDebounce)
this.searchDebounce = setTimeout(async () => {
this.searchOffset = 0
this.searchResults = await this.search()
}, 100)
},
/** Call API to search for inputted term */
async search () {
const response = await axios.get(`${this.baseUrl}/search`, { params: { term: this.searchTerm, offset: this.searchOffset } })
this.numHits = response.data.hits.total
return response.data.hits.hits
},
/** Get next page of search results */
async nextResultsPage () {
if (this.numHits > 10) {
this.searchOffset += 10
if (this.searchOffset + 10 > this.numHits) { this.searchOffset = this.numHits - 10}
this.searchResults = await this.search()
document.documentElement.scrollTop = 0
}
},
/** Get previous page of search results */
async prevResultsPage () {
this.searchOffset -= 10
if (this.searchOffset < 0) { this.searchOffset = 0 }
this.searchResults = await this.search()
document.documentElement.scrollTop = 0
}
}
})
这个应用程序非常简单 —— 我们只定义了一些共享的数据属性,以及添加了检索和分页搜索结果的方法。为防止每次按键一次都调用 API,搜索输入有一个 100 毫秒的除颤功能。
解释 Vue.js 是如何工作的已经超出了本教程的范围,如果你使用过 Angular 或者 React,其实一些也不可怕。如果你完全不熟悉 Vue,想快速了解它的功能,我建议你从官方的快速指南入手 —— https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/
7.1 - HTML
使用以下的内容替换 /public/index.html 文件中的占位符,以便于加载我们的 Vue.js 应用程序和设计一个基本的搜索界面。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Elastic Library</title>
<meta name="description" content="Literary Classic Search Engine.">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/normalize/7.0.0/normalize.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<link href="https://cdn.muicss.com/mui-0.9.20/css/mui.min.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=EB+Garamond:400,700|Open+Sans" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="app-container" id="vue-instance">
<!-- Search Bar Header -->
<div class="mui-panel">
<div class="mui-textfield">
<input v-model="searchTerm" type="text" v-on:keyup="onSearchInput()">
<label>Search</label>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Search Metadata Card -->
<div class="mui-panel">
<div class="mui--text-headline">{{ numHits }} Hits</div>
<div class="mui--text-subhead">Displaying Results {{ searchOffset }} - {{ searchOffset + 9 }}</div>
</div>
<!-- Top Pagination Card -->
<div class="mui-panel pagination-panel">
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="prevResultsPage()">Prev Page</button>
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="nextResultsPage()">Next Page</button>
</div>
<!-- Search Results Card List -->
<div class="search-results" ref="searchResults">
<div class="mui-panel" v-for="hit in searchResults" v-on:click="showBookModal(hit)">
<div class="mui--text-title" v-html="hit.highlight.text[0]"></div>
<div class="mui-divider"></div>
<div class="mui--text-subhead">{{ hit._source.title }} - {{ hit._source.author }}</div>
<div class="mui--text-body2">Location {{ hit._source.location }}</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Bottom Pagination Card -->
<div class="mui-panel pagination-panel">
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="prevResultsPage()">Prev Page</button>
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="nextResultsPage()">Next Page</button>
</div>
<!-- INSERT BOOK MODAL HERE -->
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.muicss.com/mui-0.9.28/js/mui.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.5.3/vue.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/axios/0.17.0/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
7.2 - CSS
添加一个新文件 /public/styles.css,使用一些自定义的 UI 样式。
body { font-family: 'EB Garamond', serif; }
.mui-textfield > input, .mui-btn, .mui--text-subhead, .mui-panel > .mui--text-headline {
font-family: 'Open Sans', sans-serif;
}
.all-caps { text-transform: uppercase; }
.app-container { padding: 16px; }
.search-results em { font-weight: bold; }
.book-modal > button { width: 100%; }
.search-results .mui-divider { margin: 14px 0; }
.search-results {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-around;
}
.search-results > div {
flex-basis: 45%;
box-sizing: border-box;
cursor: pointer;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.search-results > div { flex-basis: 100%; }
}
.paragraphs-container {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-bottom: 48px;
}
.paragraphs-container .mui--text-body1, .paragraphs-container .mui--text-body2 {
font-size: 1.8rem;
line-height: 35px;
}
.book-modal {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
padding: 40px 10%;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: white;
overflow-y: scroll;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
.pagination-panel {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}
.title-row {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: flex-end;
}
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.title-row{
flex-direction: column;
text-align: center;
align-items: center
}
}
.locations-label {
text-align: center;
margin: 8px;
}
.modal-footer {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
background: white;
}
7.3 - 尝试输出
在你的浏览器中打开 localhost:8080,你将看到一个简单的带结果分页功能的搜索界面。在顶部的搜索框中尝试输入不同的关键字来查看它们的搜索情况。

你没有必要重新运行
docker-compose up命令以使更改生效。本地的public目录是装载在我们的 Nginx 文件服务器容器中,因此,在本地系统中前端的变化将在容器化应用程序中自动反映出来。
如果你尝试点击任何搜索结果,什么反应也没有 —— 因为我们还没有为这个应用程序添加进一步的相关功能。
8 - 分页预览
如果能点击每个搜索结果,然后查看到来自书中的内容,那将是非常棒的体验。
8.0 - 添加 Elasticsearch 查询
首先,我们需要定义一个简单的查询去从给定的书中获取段落范围。
在 server/search.js 文件中添加如下的函数到 module.exports 块中。
/** Get the specified range of paragraphs from a book */
getParagraphs (bookTitle, startLocation, endLocation) {
const filter = [
{ term: { title: bookTitle } },
{ range: { location: { gte: startLocation, lte: endLocation } } }
]
const body = {
size: endLocation - startLocation,
sort: { location: 'asc' },
query: { bool: { filter } }
}
return client.search({ index, type, body })
}
这个新函数将返回给定的书的开始位置和结束位置之间的一个排序后的段落数组。
8.1 - 添加 API 端点
现在,我们将这个函数链接到 API 端点。
添加下列内容到 server/app.js 文件中最初的 /search 端点下面。
/**
* GET /paragraphs
* Get a range of paragraphs from the specified book
* Query Params -
* bookTitle: string under 256 characters
* start: positive integer
* end: positive integer greater than start
*/
router.get('/paragraphs',
validate({
query: {
bookTitle: joi.string().max(256).required(),
start: joi.number().integer().min(0).default(0),
end: joi.number().integer().greater(joi.ref('start')).default(10)
}
}),
async (ctx, next) => {
const { bookTitle, start, end } = ctx.request.query
ctx.body = await search.getParagraphs(bookTitle, start, end)
}
)
8.2 - 添加 UI 功能
现在,我们的新端点已经就绪,我们为应用程序添加一些从书中查询和显示全部页面的前端功能。
在 /public/app.js 文件的 methods 块中添加如下的函数。
/** Call the API to get current page of paragraphs */
async getParagraphs (bookTitle, offset) {
try {
this.bookOffset = offset
const start = this.bookOffset
const end = this.bookOffset + 10
const response = await axios.get(`${this.baseUrl}/paragraphs`, { params: { bookTitle, start, end } })
return response.data.hits.hits
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
},
/** Get next page (next 10 paragraphs) of selected book */
async nextBookPage () {
this.$refs.bookModal.scrollTop = 0
this.paragraphs = await this.getParagraphs(this.selectedParagraph._source.title, this.bookOffset + 10)
},
/** Get previous page (previous 10 paragraphs) of selected book */
async prevBookPage () {
this.$refs.bookModal.scrollTop = 0
this.paragraphs = await this.getParagraphs(this.selectedParagraph._source.title, this.bookOffset - 10)
},
/** Display paragraphs from selected book in modal window */
async showBookModal (searchHit) {
try {
document.body.style.overflow = 'hidden'
this.selectedParagraph = searchHit
this.paragraphs = await this.getParagraphs(searchHit._source.title, searchHit._source.location - 5)
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
},
/** Close the book detail modal */
closeBookModal () {
document.body.style.overflow = 'auto'
this.selectedParagraph = null
}
这五个函数提供了通过页码从书中下载和分页(每次十个段落)的逻辑。
现在,我们需要添加一个 UI 去显示书的页面。在 /public/index.html 的 <!-- INSERT BOOK MODAL HERE --> 注释下面添加如下的内容。
<!-- Book Paragraphs Modal Window -->
<div v-if="selectedParagraph" ref="bookModal" class="book-modal">
<div class="paragraphs-container">
<!-- Book Section Metadata -->
<div class="title-row">
<div class="mui--text-display2 all-caps">{{ selectedParagraph._source.title }}</div>
<div class="mui--text-display1">{{ selectedParagraph._source.author }}</div>
</div>
<br>
<div class="mui-divider"></div>
<div class="mui--text-subhead locations-label">Locations {{ bookOffset - 5 }} to {{ bookOffset + 5 }}</div>
<div class="mui-divider"></div>
<br>
<!-- Book Paragraphs -->
<div v-for="paragraph in paragraphs">
<div v-if="paragraph._source.location === selectedParagraph._source.location" class="mui--text-body2">
<strong>{{ paragraph._source.text }}</strong>
</div>
<div v-else class="mui--text-body1">
{{ paragraph._source.text }}
</div>
<br>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Book Pagination Footer -->
<div class="modal-footer">
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="prevBookPage()">Prev Page</button>
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="closeBookModal()">Close</button>
<button class="mui-btn mui-btn--flat" v-on:click="nextBookPage()">Next Page</button>
</div>
</div>
再次重启应用程序服务器(docker-compose up -d --build),然后打开 localhost:8080。当你再次点击搜索结果时,你将能看到关键字附近的段落。如果你感兴趣,你现在甚至可以看这本书的剩余部分。

祝贺你!你现在已经完成了本教程的应用程序。
你可以去比较你的本地结果与托管在这里的完整示例 —— https://search.patricktriest.com/ 。
9 - Elasticsearch 的缺点
9.0 - 耗费资源
Elasticsearch 是计算密集型的。官方建议 运行 ES 的机器最好有 64 GB 的内存,强烈反对在低于 8 GB 内存的机器上运行它。Elasticsearch 是一个 内存中 数据库,这样使它的查询速度非常快,但这也非常占用系统内存。在生产系统中使用时,他们强烈建议在一个集群中运行多个 Elasticsearch 节点,以实现高可用、自动分区和一个节点失败时的数据冗余。
我们的这个教程中的应用程序运行在一个 $15/月 的 GCP 计算实例中( search.patricktriest.com),它只有 1.7 GB 的内存,它勉强能运行这个 Elasticsearch 节点;有时候在进行初始的数据加载过程中,整个机器就 ”假死机“ 了。在我的经验中,Elasticsearch 比传统的那些数据库,比如,PostgreSQL 和 MongoDB 耗费的资源要多很多,这样会使托管主机的成本增加很多。
9.1 - 与数据库的同步
对于大多数应用程序,将数据全部保存在 Elasticsearch 并不是个好的选择。可以使用 ES 作为应用程序的主要事务数据库,但是一般不推荐这样做,因为在 Elasticsearch 中缺少 ACID,如果大量读取数据的时候,它能导致写操作丢失。在许多案例中,ES 服务器更多是一个特定的角色,比如做应用程序中的一个文本搜索功能。这种特定的用途,要求它从主数据库中复制数据到 Elasticsearch 实例中。
比如,假设我们将用户信息保存在一个 PostgreSQL 表中,但是用 Elasticsearch 去提供我们的用户搜索功能。如果一个用户,比如,“Albert”,决定将他的名字改成 “Al”,我们将需要把这个变化同时反映到我们主要的 PostgreSQL 数据库和辅助的 Elasticsearch 集群中。
正确地集成它们可能比较棘手,最好的答案将取决于你现有的应用程序栈。这有多种开源方案可选,从 用一个进程去关注 MongoDB 操作日志 并自动同步检测到的变化到 ES,到使用一个 PostgresSQL 插件 去创建一个定制的、基于 PSQL 的索引来与 Elasticsearch 进行自动沟通。
如果没有有效的预构建选项可用,你可能需要在你的服务器代码中增加一些钩子,这样可以基于数据库的变化来手动更新 Elasticsearch 索引。最后一招,我认为是一个最后的选择,因为,使用定制的业务逻辑去保持 ES 的同步可能很复杂,这将会给应用程序引入很多的 bug。
让 Elasticsearch 与一个主数据库同步,将使它的架构更加复杂,其复杂性已经超越了 ES 的相关缺点,但是当在你的应用程序中考虑添加一个专用的搜索引擎的利弊得失时,这个问题是值的好好考虑的。
总结
在很多现在流行的应用程序中,全文搜索是一个非常重要的功能 —— 而且是很难实现的一个功能。对于在你的应用程序中添加一个快速而又可定制的文本搜索,Elasticsearch 是一个非常好的选择,但是,在这里也有一个替代者。Apache Solr 是一个类似的开源搜索平台,它是基于 Apache Lucene 构建的,与 Elasticsearch 的核心库是相同的。Algolia 是一个搜索即服务的 Web 平台,它已经很快流行了起来,并且它对新手非常友好,很易于上手(但是作为折衷,它的可定制性较小,并且使用成本较高)。
“搜索” 特性并不是 Elasticsearch 唯一功能。ES 也是日志存储和分析的常用工具,在一个 ELK(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)架构配置中通常会使用它。灵活的全文搜索功能使得 Elasticsearch 在数据量非常大的科学任务中用处很大 —— 比如,在一个数据集中正确的/标准化的条目拼写,或者为了类似的词组搜索一个文本数据集。
对于你自己的项目,这里有一些创意。
- 添加更多你喜欢的书到教程的应用程序中,然后创建你自己的私人图书馆搜索引擎。
- 利用来自 Google Scholar 的论文索引,创建一个学术抄袭检测引擎。
- 通过将字典中的每个词索引到 Elasticsearch,创建一个拼写检查应用程序。
- 通过将 Common Crawl Corpus 加载到 Elasticsearch 中,构建你自己的与谷歌竞争的因特网搜索引擎(注意,它可能会超过 50 亿个页面,这是一个成本极高的数据集)。
- 在 journalism 上使用 Elasticsearch:在最近的大规模泄露的文档中搜索特定的名字和关键词,比如, Panama Papers 和 Paradise Papers。
本教程中应用程序的源代码是 100% 公开的,你可以在 GitHub 仓库上找到它们 —— https://github.com/triestpa/guttenberg-search
我希望你喜欢这个教程!你可以在下面的评论区,发表任何你的想法、问题、或者评论。
作者简介:
全栈工程师,数据爱好者,学霸,“构建强迫症患者”,探险爱好者。
via: https://blog.patricktriest.com/text-search-docker-elasticsearch/
作者:Patrick Triest 译者:qhwdw 校对:wxy
